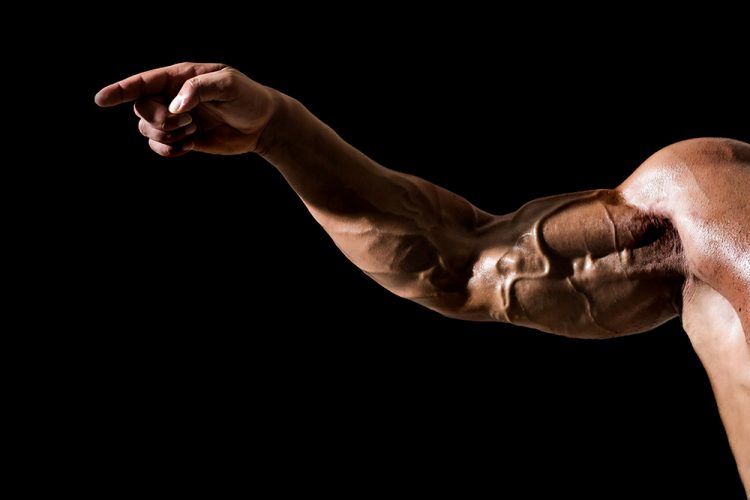
Vascularity, as it is commonly used in fitness, refers to the visibility of blood vessels on the skin. It does not have any actual benefits, but it increases the aesthetic appeal of bodybuilders and is a sign of muscularity and low body fat percentage. Improving vascularity requires hard work and a good understanding of anatomic processes that lead to the increased size of blood vessels.
Combining cardiovascular exercise and strength training along with a healthy diet, sufficient water intake, and intake of additional supplements will improve the body’s overall vascularity.
This article will discuss the factors that affect vascularity and explain the processes involved in increasing vascularity. It will also give pointers to apply the understanding of these factors on workout and diet routines to improve vascularity.
Factors Affecting Vascularity
Body Fat Percentage
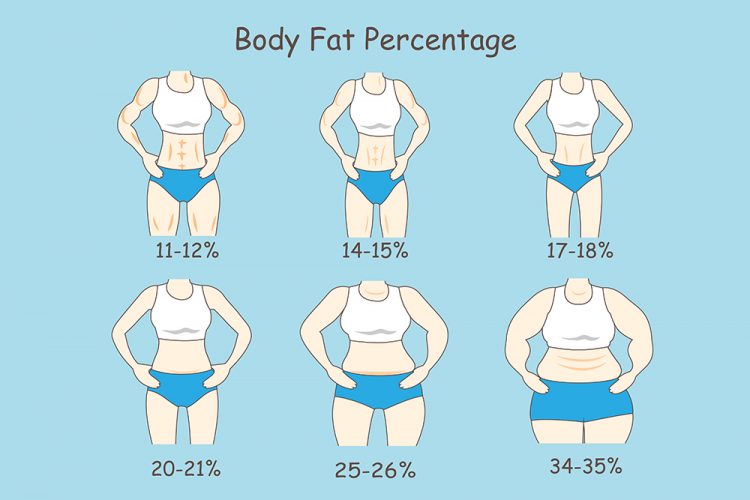
Body fat percentage affects vascularity as subcutaneous fat, or the layer of fat under the skin, can hide the superficial veins. An overweight individual can have a harder time developing vascularity due to the thick layer of subcutaneous fat preventing the superficial vein from manifesting onto the skin, even as heart rate rises through exercise.
Maintaining a good muscle-to-fat ratio can help in reducing the amount of subcutaneous fat as well as push the superficial vein to the surface of the skin. A combination of strength training and cardiovascular exercise can help achieve optimal muscle-to-fat ratio.
The ideal body fat percentage for vascularity is around 8%. This body fat percentage will manifest vascularity around the body, even when the blood vessels are in a relaxed state. It is also a good standard to follow for displaying competition-level vascularity.
People with 10-12% body fat percentage can also have good vascularity, especially after a workout. At this body fat percentage, the cephalic vein, or the prominent bicep vein, can manifest after a workout too.
Moreover, people who have 15%+ body fat percentage need to combine strength training, cardio, and diet changes to lower their body fat percentage in order to have visible vascularity.
Women also have to engage in these exercises and lifestyle habits to achieve vascularity because they naturally have less muscle and more fat than men.
Muscle Mass
Along with body fat percentage, muscle mass, or the overall weight of the muscles in the body, also affects vascularity. Bigger muscles help in pushing the superficial vein to the surface of the skin, which becomes more prominent with less subcutaneous fat.
Blood vessels become dilated through vasodilation, or expansion of the blood vessels, when working out. It also remains dilated for a certain period of time after working out. Repeated vasodilation can cause the blood vessels to remain dilated even as the blood vessels revert to a rested state.
To showcase optimal vascularity, it is best to take photos of the body at around 15-20 minutes after a workout. This takes advantage of the remaining vasodilation, especially for people who are still working on their muscle-to-fat ratio. For more permanent vascularity, however, alternating between mass building and fat burning routines can help improve vascularity.
Water Retention
Water retention refers to the process of absorbing water into the cells. High water retention can lead to puffiness of the subcutaneous layer of the skin which can hinder vascularity.
Water retention occurs as an adaptation to low water levels in the body. High sodium concentration in the body can also cause water retention because sodium brings water with it as it is absorbed into the cells.
High stress levels or high concentration of the cortisol hormone can also cause water retention along with high aldosterone hormone levels. Aldosterone is responsible for maintaining a balance between sodium and potassium in the body.
Some of the symptoms of water retention include bloatedness, swollen legs, puffiness, and stiff joints. It can also cause weight fluctuations, which is a great concern for bodybuilders and professional athletes.
Ways to Improve Vascularity
Diet
An ideal diet for improving vascularity is comprised of a macro-nutrient balance of high protein, low carbs, and high fat.
Protein helps in building muscle mass and can be obtained from both animal and plant sources. A high-protein diet is usually composed of foods like meat, egg, beans, nuts, and seafood.
Carbohydrate consumption for greater mass gain and fat loss should be composed of complex carbohydrates found in sweet potatoes and brown rice. Simple carbohydrates in pasta and white rice can cause accumulation of subcutaneous and visceral fat which can hinder vascularity.
Fat will act as the balancing mechanism between protein and carbohydrates to ensure a gradual caloric deficit to facilitate steady mass gain and weight loss. Intake of healthy fat found in fruits like avocado and coconut. Nuts like macadamia and walnuts also have high healthy fat content.
An overweight individual should aim to reduce 0.5 to 1.5 pounds of excess weight per week until he/she achieves a good muscle-to-fat ratio at an ideal weight. This can be achieved through a caloric deficit of 300-500 calories from your recommended caloric intake per day.
Hydration
Lowering water retention requires the balancing of sodium and potassium in the body. Sodium can cause water retention while potassium can flush the water out from the cells. The Institute of Medicine recommends a maximum of 2300mg of sodium and 4700mg of potassium per day.
Drinking plenty of water can prevent water retention in cells. The recommended water intake is 3/4 gallon to 1 gallon of water per day for adults, with an addition of 1 to 1.5 liters per hour of workout. This can also be combined with a low-carb diet to greatly improve vascularity.
Certain hydration routines can also help in lowering water retention on specific days. Professional athletes and bodybuilders perform these routines in preparation for upcoming competitions or events.
An example hydration routine involves a loading phase of 4-5 days where the person drinks over 5 liters of water per day. Then, for the next two days, he/she will cut back on water intake or barely drink any water. On the day of the event, the person can drink wine to further reduce water retention
Diuretics can also help expel water and sodium from the body. Natural diuretics include coffee, celery, eggplant, and onion. However, water is usually taken with caffeine which counters its effects as a diuretic.
Supplements for Increasing Vasodilation
Vasodilation is the process of expanding the blood vessels. Nitric Oxide (NO) is the primary hormone that facilitates vasodilation in the body. As a vasodilator, it increases blood flow into the muscles for faster transportation of oxygen. The endothelial cells produce nitric oxide during physical training.
Certain supplements function as NO precursors to increase the production of NO in the body. They help promote vasodilation and improve vascularity. Glycerol and L-citrulline are known NO precursors as well as agmatine and ornithine.
Thermogenic products such as caffeine and ginger can also increase vascularity by increasing the heat produced in the body. This widens the blood vessels and raises basal metabolic rate.
Cardio
Cardiovascular exercise and other aerobic activities promote fat loss by helping achieve a daily caloric deficit and reducing body fat percentage. These are essential factors for improving vascularity.
Cardio can also increase blood pressure as the heart pumps more blood into the various parts of the body. This promotes cell swelling and expands the blood vessels.
While this can increase capillary density or size of the blood vessels, it can also produce smaller blood vessels which can also improve vascularity.
“Pump” Workout Routines
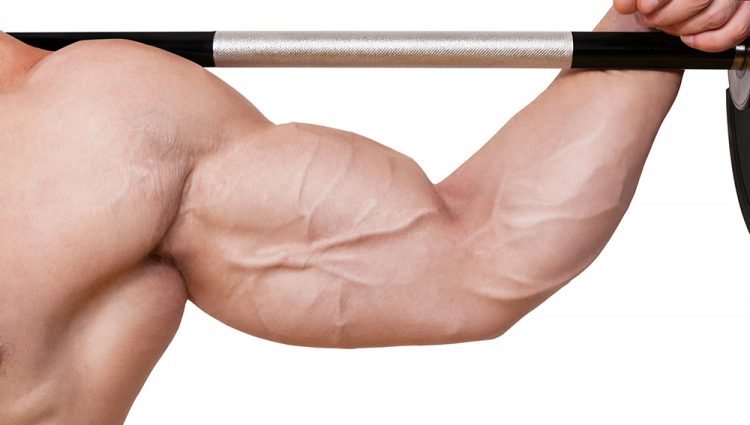

Pump workout routines, which facilitate metabolite accumulation and cell swelling, can help increase metabolic stress on the muscles. Greater metabolic stress stimulates the production of nitric oxide in the body which increases muscle endurance over time. Pump workouts are usually characterized by high repetition at reduced weights with short rests in between each set.
A nine-month vascular program, moreover, can provide the best workout structure to achieve optimal vascularity. These vascular programs are composed of three phases namely: strength and hypertrophy phase, fat loss phase, and shredding phase. Each of these phases lasts three months and works on building muscle mass and fat loss.
Blood Flow Restriction Training (BFRT)
Blood Flow Restriction Training (BFRT) aims to increase vascularity in specific parts of the body. Blood Flow Restriction increases the size of the blood vessels by partially restricting blood flow back to the heart and pooling blood in blood vessels in specific parts of the body.
The common pump routine performed with BFRT includes four sets of leg extensions, tricep dips, and bicep curls with 10-15 repetitions and 30 seconds of rest in between sets.
Circulatory restriction methods can increase muscle size and vascularity. However, these circulatory inhibiting methods can be detrimental and dangerous if performed excessively.
Final Thoughts
The various requirements on body fat, muscle mass, water retention, and diet make improving vascularity a great challenge, especially for those who do not possess the genetics for vascularity. More importantly, improving vascularity takes time as it often comes as the final touch in a well-defined muscular physique.

